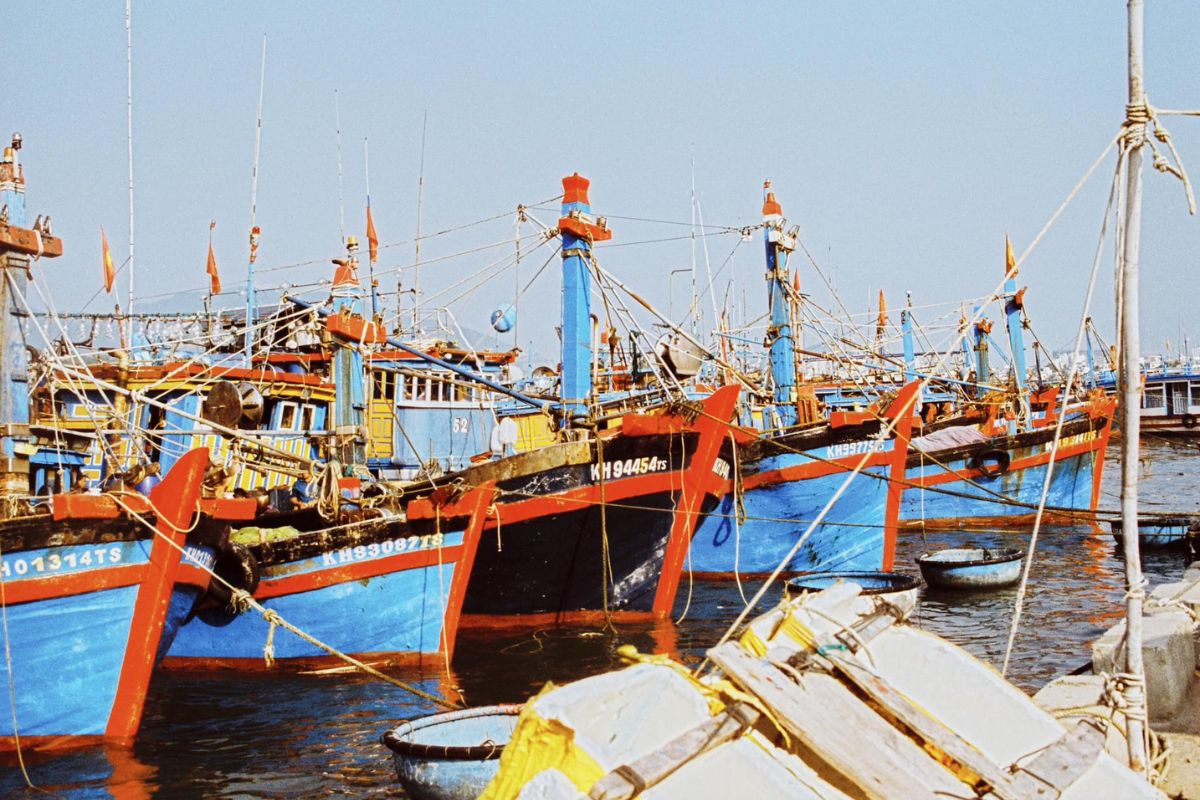
Sustainable fisheries exploitation associated with marine ecosystem protection
In the context of global fisheries resources facing the risk of depletion due to overexploitation, the application of sustainable and environmentally friendly fishing methods is more urgent than ever.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), about 34% of global fisheries resources are currently overexploited. This article will introduce environmentally friendly fishing methods, ensuring the sustainable development of the fisheries industry while protecting marine ecosystems.
1. Handline and longline methods
Handline and longline methods are considered one of the most environmentally friendly fishing methods. The characteristics of this method are:
– High selectivity: Fishermen can select individuals to catch, minimizing the catching of non-target species.
– Low impact on the seabed: Does not disturb the seabed and sensitive ecosystems.
– High quality fish: The fish are often caught alive and with little damage, ensuring product quality.
In many countries such as Japan and Iceland, seafood products caught by this method are often highly valued and have great economic value.
2. Purse nets with escape points and dolphin-friendly nets
Purse nets are one of the fishing methods commonly used in the seafood industry. When implementing this method, fishermen will use a large net and surround the school of fish, then pull the net back to catch the fish. This method, if applied properly, can help minimize the capture of non-target species. Moreover, purse seine nets can be used to catch small fish or fish in large numbers, helping to optimize production and reduce the impact on the marine ecosystem.
Traditional purse seine nets often cause a lot of harm to non-target species such as dolphins and sea turtles. Improvements include:
– Escape nets: Designed with escape hatches that allow non-target species to escape.
– Dolphin-friendly nets: Designed to reduce bycatch of dolphins and other marine mammals.
– Reduced catch time: Shorten the catch time to reduce bycatch mortality.
Standards such as “Dolphin-Safe” have become important marks in the global seafood market.
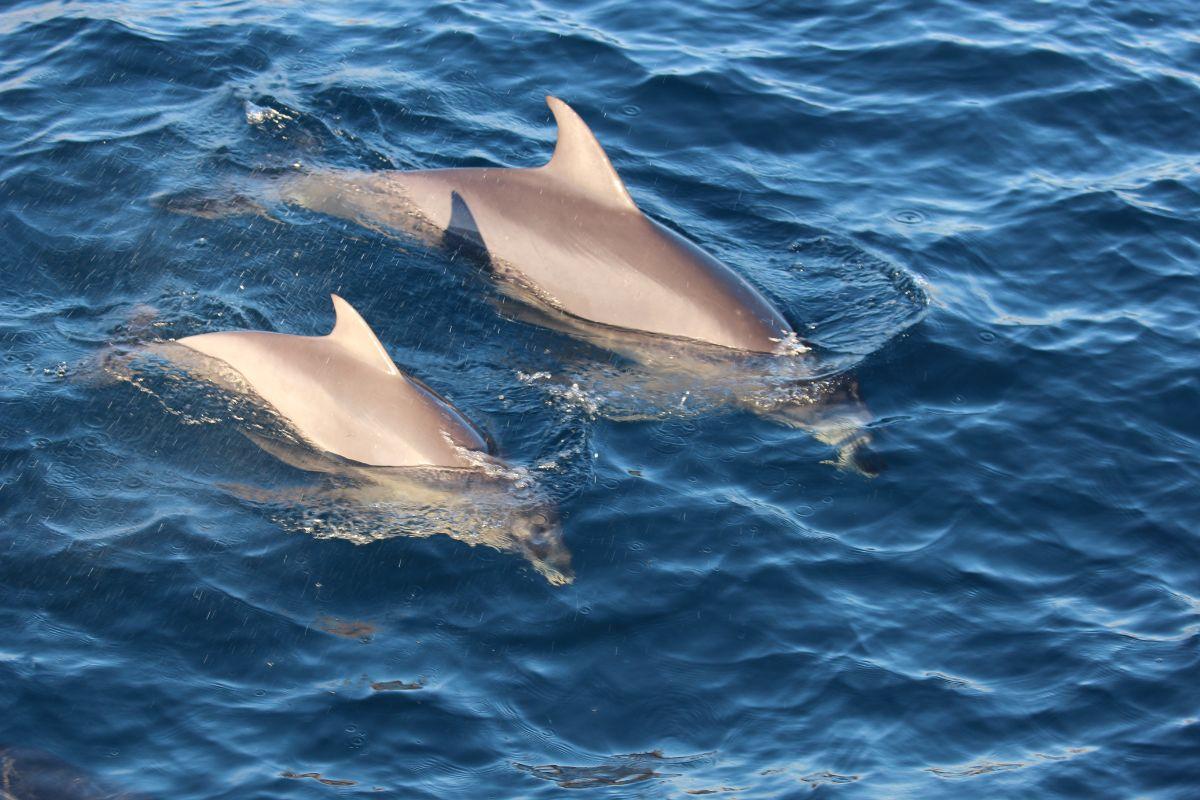

Traditional purse seine nets often cause harm to non-target species such as dolphins and sea turtles.
3. Improved traps
Improved traps are a highly selective and low-impact fishing method:
– Friendly design: Traps are designed with escape hatches for non-target species.
– Biodegradable materials: Use biodegradable materials to reduce plastic waste in the ocean.
– “Ghost” traps: Modern traps are designed to open or decompose after a certain period of time if lost, avoiding the phenomenon of “ghost fishing” that is harmful to marine life.
In Vietnam, some fishermen in Quang Ninh and Hai Phong have begun to apply these improved traps.
4. Seasonal and regional fishing
To ensure the sustainable development of aquatic resources, many countries have applied regulations on seasonal fishing and restricted areas. This can help aquatic species have time to reproduce and grow, while protecting particularly sensitive or high-conservation areas such as marine reserves or coral reef areas. Seasonal fishing not only helps maintain aquatic resources, but also creates conditions for aquatic species to regenerate and recover.
This approach focuses on managing the time and space of fishing:
– Observing the breeding season: Avoid fishing during the breeding season of aquatic species to ensure that populations are maintained.
– Establishing marine reserves: Identifying areas where fishing is prohibited or restricted to protect important ecosystems.
– Rotation of fishing areas: Applying a rotation regime to allow areas to recover after a period of exploitation.
In the Philippines, this model has helped restore many coral reefs and increase catches in areas adjacent to protected areas.
5. Modern technology in sustainable fishing
Modern technology, such as the use of satellite monitoring systems, sensors and big data, is gradually being applied to the fisheries industry to monitor and manage fishing. These tools help to accurately track fishing areas, ensure compliance with regulations on fishing areas and times. Technology also helps to detect illegal fishing activities and support more effective protection of aquatic resources.
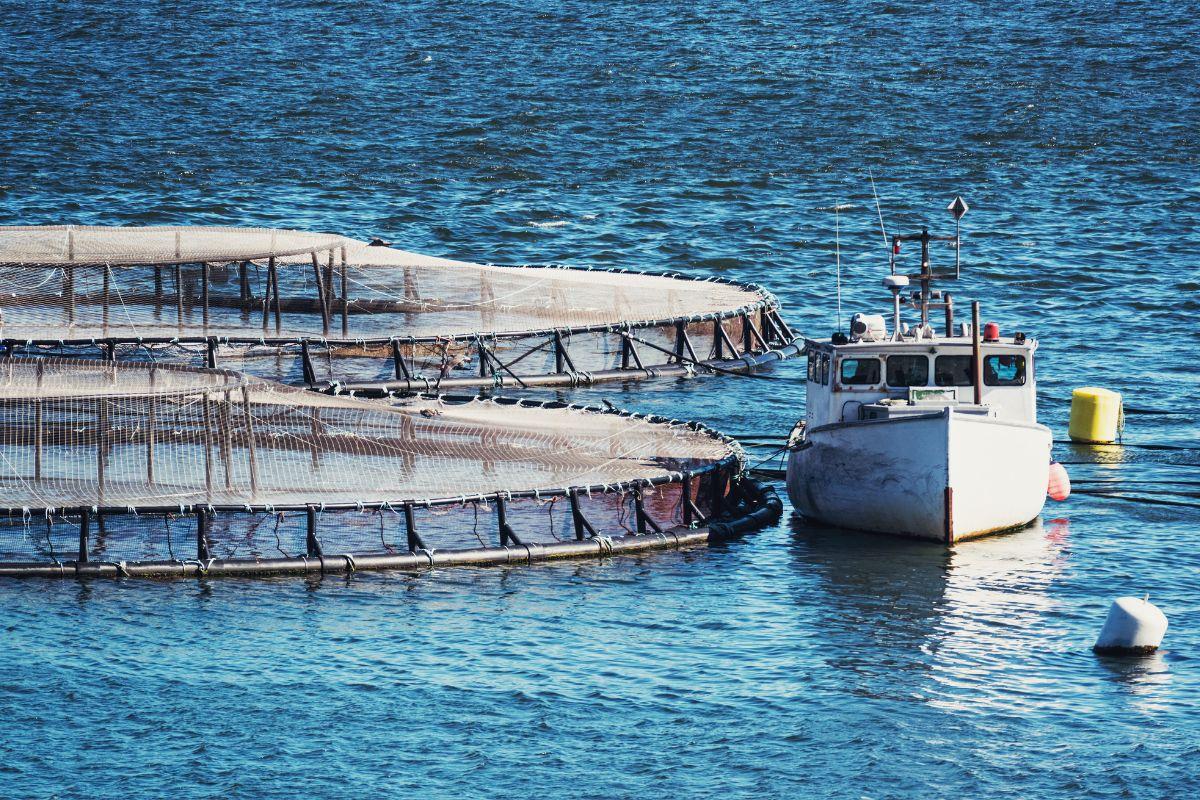

Modern technology, such as the use of satellite monitoring systems, sensors and big data, is gradually being applied to the fisheries industry.
Technology plays an important role in developing sustainable fishing methods:
– Bycatch Reduction Devices (BRDs): Devices installed in nets to reduce the capture of non-target species.
– Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs): Helps sea turtles escape from fishing nets.
– Electronic monitoring systems: Track fishing activities to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
– Precise fish school positioning technology: Helps reduce search time, save fuel and reduce carbon emissions.
Many developed countries such as Norway and Iceland have widely applied these technologies in their fishing industry.
6. Sustainable fishing certification
Today, many fishermen and seafood businesses have implemented sustainable fishing certifications, such as certification by the MSC (Marine Stewardship Council). This certification demonstrates that seafood is caught from sustainable sources, does not harm the marine environment, and is responsible for protecting aquatic species and marine ecosystems. Applying these certifications helps fishermen comply with environmental protection regulations and promotes responsible seafood consumption.
Certification programs play an important role in promoting sustainable fishing methods:
– MSC (Marine Stewardship Council) certification: One of the most prestigious certifications for sustainable fishing.
– ASC (Aquaculture Stewardship Council) certification: Focuses on the sustainability of aquaculture.
– Friend of the Sea certification: International certification for products from sustainable fisheries and aquaculture.
These certifications not only protect the environment but also bring economic benefits to fishermen through access to high-value markets.
7. Science and Data-Based Fishing
The application of science and data in fisheries management helps ensure sustainability:
– Set catch quotas (TAC): Based on scientific research on populations to determine maximum sustainable catch.
– Regular stock assessment: Continuously monitor fish stocks to adjust fishing plans.
– Research collaboration: Combining traditional knowledge of fishermen with modern scientific research.
New Zealand and Australia are pioneers in applying science-based fisheries management models.
8. Co-management and the role of fishing communities
The participation of fishing communities in fisheries resource management is an important factor:
– Co-management model: Cooperation between government and fishing communities in resource management.
– Indigenous knowledge: Taking advantage of traditional knowledge of local fishermen about marine ecosystems.
– Education and awareness raising: Training fishermen on sustainable fishing methods and the impacts of overfishing.
In Vietnam, the co-management model has been successfully applied in some localities such as Quang Nam and Binh Dinh.
Applying sustainable and environmentally friendly fishing methods not only protects the marine ecosystem but also ensures long-term livelihoods for fishing communities. The combination of traditional methods, modern technology, and appropriate management policies will contribute to building a sustainable fisheries industry for the future.
In the context of globalization and climate change, the transition to sustainable fishing methods is not only the responsibility of one country but requires international cooperation. Each consumer also plays an important role by choosing seafood products with sustainable certification, creating market incentives for positive change in the fishing industry.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
